Microsoft Excel is used in calculating or for data comprehension. It comprises of
book, sheet and page. cell is located in the Microsoft excel it’s the combination
of row and column.
Component OF Microsoft
Excel
· Menu bar
· Tool bar
· Title bar
Ø Title bar:
Its the title
name of your work
Ø Menu bar: just as that of the
Microsoft word excel consist of home, insert, page layout, review and view. The
only difference is the present of data and formulas in the menu bar.
Ø Tool bar: is consist of the tools
needed to work on the Microsoft word excel
· Home :
· Clipboard: it consists of the cut,
copy, paste and format paint.
· Font: it is used in changing the font
style and it consists of bold, underline, italic, grow font, font style, shrink
font etc.
· Alignment: it is used in the
arrangement of your work.
· Numbers: it is used in other to know
how the value of your work should be arranged.
Insert:
ü Table: it is used to create table on
the Microsoft excel.
ü Illustration: it consists of picture,
shapes, smart art and clip art.
ü Chart: it is used in documentation of
your work using diagram.
ü Text: it is used in
the arrangement of the heading.
FORMULAS
Formulas are known as a mathematical
way of solving mathematical problem or technical problem.
Types of formulas
1. Relative formulas
2. Absolute formulas
3. Mix formulas
v Relative formulas: it uses referees
in a way which allow in a1 and a2 to combine in other to get result. E.g.
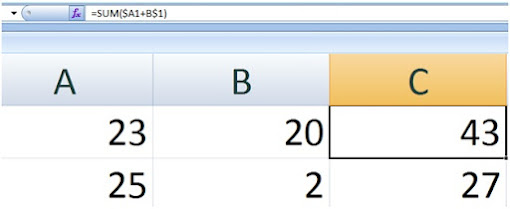
Notice the big circle in it you see a writing that looks like
this =sum(A1+B1) ,in the table above you will also notice it is divided into
three places A,B,C in other to get C we had to add A and B using the relative
formulas.
vAbsolute formulas: it uses referees and dollar sign in order to solve mathematical problem.
Just as that of relative we had to use A and B in order to get C the any
difference is the present of the dollar sign.
vMix formulas: it uses dollar sign in the beginning and in the center
OTHER
TYPES OF FORMULAS THAT ARE USED IN MICROSOFT EXCEL.
1.
=IF
2.
=AVERAGE
3.
=MIN
4.
=MAX
5.
=SUMproduct
6.
=PRODUCT
7.
=DIVISION ETC.
LOGICAL
FUNCTION
It This consists of:
· AND GATE
· OR GATE
Ø And gate: it states that all condition must be true to produce
true statement.
Or gate: is state that one condition
must be true to produce true.
Note: the line found in Microsoft
excel is known as GRIDLINES
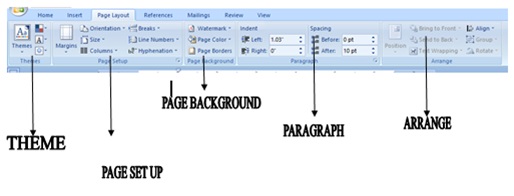
· PAGE LAYOUT:
This is used in formatting of your page
Duration: 1 Day (4 hours teaching + 1 hour assessment)
Class Level: Beginners / Students new to Excel
Lesson
Objectives
By the end of the lesson, students
should be able to:
- Understand the Excel environment (workbook, worksheet,
rows, columns, and cells).
- Enter and format basic data in Excel.
- Identify and explain the main Excel ribbon menus (Home,
Insert, Page Layout, Formulas, Data, Review, View).
- Use at least 2 tools from each tab to create, format, and
analyze data.
- Complete a practical test using Excel menus.
Teaching
Steps
🕐
Hour 1: Introduction to Excel + Home Tab
Explain:
- Excel = spreadsheet program for data entry,
calculations, charts.
- Workbook (entire file) vs Worksheet (single sheet).
- Rows (numbers), Columns (letters), Cells
(intersection).
Example:
Type this table in Excel:
|
Name |
Age |
Class |
|
John |
10 |
Basic 4 |
|
Mary |
11 |
Basic 5 |
Class Activity:
- Students enter names, ages, and classes of 5
classmates.
- Save file as ClassRecord.xlsx.
Then, Home Tab Features:
- Clipboard (copy, paste), Font (bold, italics),
Alignment (center), Number (currency), Styles (table formatting).
- Format the ClassRecord table: make headers bold,
center-align, and give Age column number format.
🕑
Hour 2: Insert Tab
Explain:
- Insert Tables, Pictures, Shapes, Charts.
Example:
Create a sales table:
|
Product |
Sales |
|
Rice |
50 |
|
Beans |
40 |
|
Maize |
30 |
Insert → Column Chart.
Activity:
Students create their own sales table with 5 items and insert a Pie Chart.
🕒
Hour 3: Page Layout & Formulas
Page Layout:
- Themes, Margins, Orientation (Portrait/Landscape),
Print Setup.
Formulas (basic):
- =SUM() → adds numbers.
- =AVERAGE() → finds mean.
Example:
Marks table:
|
Student |
English |
Math |
Science |
|
John |
60 |
70 |
65 |
|
Mary |
80 |
75 |
85 |
- Use =SUM(B2:D2) for John’s Total.
- Use =AVERAGE(B2:D2) for John’s Average.
- Change page orientation to Landscape.
Activity:
Students create their own marks table for 4 classmates, calculate totals &
averages, then change orientation.
🕓
Hour 4: Data, Review & View Tabs
Data:
- Sort (A–Z, Z–A), Filter.
Review:
- Spelling check, Add Comments.
View:
- Normal vs Page Layout view, Zoom, Freeze Panes.
Example:
Enter student names + marks.
- Sort by marks (highest → lowest).
- Add a comment (“Excellent”) on highest score.
- Freeze top row.
Activity:
Students create a product list (6 products + prices).
- Sort prices highest to lowest.
- Add a comment to most expensive item.
- Freeze the header row.
🕔
Hour 5: Assessment (Practical, 10 Marks)
- Create a table of 5 products and prices (Home tab) → 2
marks.
- Insert a chart from the table (Insert tab) → 2 marks.
- Use =SUM() to calculate total price (Formulas tab) → 2 marks.
- Change page to Landscape (Page Layout) → 2 marks.
- Sort products by price highest to lowest (Data tab) → 2
marks.
Conclusion
- Recap what Excel is and the purpose of menus.
- Ask students: “Which tab did you enjoy using the most
today?”
- Homework: Create a student score sheet with
totals, averages, and a chart.
Day
2 (Tue) – Formatting Data
Objective: Students should be able to format data neatly.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Show Bold, Italic, Underline (Home tab → Font
group).
- Show how to adjust column width & row height.
- Demonstrate cell borders and fill color.
💻
Example
- Reformat yesterday’s table:
- Headings in bold and background color yellow.
- Borders around the table.
|
Name |
Age |
Class |
|
John |
10 |
Basic 4 |
|
Mary |
11 |
Basic 5 |
🎯
Class Activity
- Students format their table from Day 1:
- Headings bold + colored.
- Add borders.
- Adjust width so all words fit.
Day
3 (Wed) – Basic Calculations
Objective: Students should perform basic arithmetic in Excel.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Explain formulas begin with = sign.
- Show addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*),
division (/).
- Introduce AutoSum (Σ button).
💻
Example
- Create sales table:
|
Item |
Price |
|
Book |
500 |
|
Pen |
100 |
|
Bag |
2000 |
👉 In another cell: =500+100+2000 or use =SUM(B2:B4) → 2600
🎯
Class Activity
- Students create 5 items with prices, calculate
total cost using both:
- Normal formula (=A+B+C...)
- SUM function.
Day
4 (Thu) – Saving & Managing Files
Objective: Students should learn to save, open, and manage multiple
sheets.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Show Save (Ctrl+S), Save As, and how to
rename files.
- Show how to insert a new worksheet.
- Explain difference between .xlsx (Excel format)
and .csv (text format).
💻
Example
- Save yesterday’s sales record as:
- Sales.xlsx
- Sales.csv
🎯
Class Activity
- Students create a worksheet with two sheets:
- Sheet1: Class Record (Day 1 work).
- Sheet2: Sales Record (Day 3 work).
- Save as StudentWorkbook.xlsx.
Day
5 (Fri) – Assessment Test
Objective: Test students’ understanding of Week 1.
📝
Test Questions
- Create a table of 5 grocery items with their
prices.
- Format the table:
- Bold headings.
- Add borders.
- Color headings with yellow background.
- Calculate the total cost using:
- Direct formula (=A+B+C…)
- SUM function.
- Save the file as GroceryTest.xlsx.
✅
Teacher’s Marking Guide
- Correct table (2 marks).
- Formatting neat (2 marks).
- Correct calculation (3 marks).
- Proper saving (3 marks).
Total = 10 marks
Perfect 👍 Let’s fully expand WEEK 2 (Functions & Charts)
with step-by-step teaching, examples, class activities, and a test on Day 5.
WEEK 2: Excel Functions & Charts (Expanded)
Day
1 (Mon) – Functions (SUM, AVERAGE, MIN, MAX)
Objective: Students should learn to use basic statistical functions.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Explain that functions are ready-made formulas
in Excel.
- Show =SUM(range), =AVERAGE(range), =MIN(range), =MAX(range).
- Use student marks as an example.
💻
Example
- Enter marks of 5 students:
|
Name |
Marks |
|
John |
65 |
|
Mary |
75 |
|
Peter |
40 |
|
Rose |
90 |
|
Paul |
55 |
- Total: =SUM(B2:B6) → 325
- Average: =AVERAGE(B2:B6)
→ 65
- Lowest: =MIN(B2:B6)
→ 40
- Highest: =MAX(B2:B6)
→ 90
🎯
Class Activity
- Students enter marks of 6 classmates, then find total,
average, lowest, highest.
Day
2 (Tue) – Text Functions (PROPER, UPPER, LOWER, CONCAT, LEFT, RIGHT)
Objective: Students should manipulate text with Excel functions.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Explain PROPER, UPPER, LOWER → change text case.
- Show CONCAT (join text).
- Show LEFT, RIGHT → extract parts of text.
💻
Example
- Enter:
|
First
Name |
Last
Name |
Phone |
|
john |
doe |
08012345678 |
- =PROPER(A2) → John
- =UPPER(B2) → DOE
- =LOWER(A2) → john
- =CONCAT(A2," ",B2) → john doe
- =LEFT(C2,4) → 0801
- =RIGHT(C2,4) → 5678
🎯
Class Activity
- Students enter 5 names and phone numbers.
- Use functions to:
- Write names in Proper Case.
- Join first and last names.
- Extract first 3 and last 4 digits of phone number.
Day
3 (Wed) – IF Function (Logic)
Objective: Students should classify data using logical functions.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Explain logic: IF checks a condition → returns True or
False.
- Syntax: =IF(condition, value_if_true, value_if_false)
- Apply to marks grading.
💻
Example
- Table:
|
Name |
Marks |
Result |
|
John |
65 |
=IF(B2>=50,"Pass","Fail")
→ Pass |
|
Mary |
45 |
→ Fail |
🎯
Class Activity
- Students create a grading table for 6 students.
- If Marks ≥ 50 → Pass, otherwise Fail.
Day
4 (Thu) – Charts
Objective: Students should create simple charts.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Explain charts help visualize data.
- Show how to create:
- Column chart
- Bar chart
- Pie chart
💻
Example
- Marks table from Day 1 → Create Column Chart
showing student marks.
🎯
Class Activity
- Students enter sales data for 5 products.
- Create:
- Column chart for sales.
- Pie chart showing percentage share.
Day
5 (Fri) – Assessment Test
Objective: Assess students’ use of functions and charts.
📝
Test Questions
- Enter the marks of 5 students.
- Use SUM, AVERAGE, MIN, MAX to analyze results.
- Add a column for Pass/Fail using IF function.
- Create a Column Chart to display student marks.
✅
Teacher’s Marking Guide
- Correct use of SUM, AVERAGE, MIN, MAX → 3 marks
- IF function applied correctly → 3 marks
- Chart created correctly → 4 marks
Total = 10 marks
👉 Now by the end of Week
2, students can:
- Use Excel functions (math, text, logic).
- Create basic charts.
Great 👍 Let’s now fully expand WEEK 3 (Accounting Excel: Cashbook,
Sales, VAT, Payroll) with step-by-step teaching, examples, class
activities, and a test on Day 5.
WEEK 3: Accounting Excel (Expanded)
Day
1 (Mon) – Cashbook in Excel
Objective: Students should understand how to record cash inflows and
outflows.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Explain that a cashbook records money received
(Debit) and money spent (Credit).
- Show columns: Date, Description, Debit, Credit,
Balance.
- Use formulas to calculate running balance.
💻
Example
|
Date |
Description |
Debit
(In) |
Credit
(Out) |
Balance |
|
01/09/25 |
Opening Bal |
5000 |
5000 |
|
|
02/09/25 |
Bought Books |
2000 |
=E2-C3 |
|
|
03/09/25 |
Fees Income |
3000 |
=E3+D4 |
👉 Running Balance Formula: =Previous Balance + Debit – Credit
🎯
Class Activity
- Students record 5 cash transactions for a small
shop and calculate daily balance.
Day
2 (Tue) – Sales & Purchases Records
Objective: Students should calculate sales totals.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Create columns: Item, Quantity, Price, Total.
- Formula for Total = Quantity × Price.
💻
Example
|
Item |
Quantity |
Price |
Total |
|
Book |
5 |
200 |
=B2*C2 → 1000 |
|
Pen |
10 |
50 |
=B3*C3 → 500 |
👉 Grand Total: =SUM(D2:D3) → 1500
🎯
Class Activity
- Students create a sales table with 5 products
and calculate total sales.
Day
3 (Wed) – VAT & Discounts
Objective: Students should calculate tax (VAT) and discount.
📝
Teaching Steps
- VAT = Total × 7.5% → =Total*0.075
- Discount = Total × 10% → =Total*0.1
- Net Amount = Total + VAT – Discount
💻
Example
|
Item |
Quantity |
Price |
Total |
VAT
(7.5%) |
Discount
(10%) |
Net
Amount |
|
Book |
5 |
200 |
1000 |
=D2*0.075 → 75 |
=D2*0.1 → 100 |
=D2+E2-F2 → 975 |
🎯
Class Activity
- Students calculate VAT and discount for 5 sales
items.
Day
4 (Thu) – Payroll in Excel
Objective: Students should prepare simple payroll.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Columns: Name, Basic Salary, Allowance, Tax, Net
Salary.
- Net Salary Formula: =Basic + Allowance – Tax.
💻
Example
|
Name |
Basic
Salary |
Allowance |
Tax |
Net
Salary |
|
John |
30000 |
5000 |
4000 |
=B2+C2-D2 → 31000 |
|
Mary |
25000 |
4000 |
3000 |
=B3+C3-D3 → 26000 |
🎯
Class Activity
- Students prepare payroll for 5 staff members.
Day
5 (Fri) – Assessment Test
Objective: Test students’ ability to handle basic accounting tasks in
Excel.
📝
Test Questions
- Create a Cashbook with 4 transactions (Debit
& Credit) and show running balance.
- Create a Sales Table for 5 items with Quantity ×
Price = Total.
- Add VAT (7.5%) and Discount (10%) to one
of the sales.
- Prepare a Payroll for 3 staff with Net Salary
calculation.
Teacher’s
Marking Guide
- Cashbook with correct running balance → 3 marks
- Sales table with total → 2 marks
- VAT & Discount applied correctly → 2 marks
- Payroll with Net Salary → 3 marks
Total = 10 marks
👉 By the end of Week 3,
students can:
- Record cashbook entries.
- Prepare sales & purchases records.
- Calculate VAT & discounts.
- Design a simple payroll sheet.
WEEK 4: Advanced Accounting Excel (Expanded)
Day
1 (Mon) – Using VLOOKUP
Objective: Students should use VLOOKUP to search for information in a
table.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Explain that VLOOKUP searches for a value in the
first column of a table and returns information from another column.
- Syntax: =VLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, col_index_num, [range_lookup])
💻
Example
- Price List:
|
Code |
Item |
Price |
|
P01 |
Book |
500 |
|
P02 |
Pen |
100 |
|
P03 |
Bag |
2000 |
👉 Formula: =VLOOKUP("P02", A2:C4, 3,
FALSE) → 100
🎯
Class Activity
- Students create a product code table.
- Use VLOOKUP to find the price of any product by
entering its code.
Day
2 (Tue) – Using HLOOKUP
Objective: Students should use HLOOKUP to search across rows.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Explain that HLOOKUP is similar to VLOOKUP but
works horizontally.
- Syntax: =HLOOKUP(lookup_value, table_array, row_index_num,
[range_lookup])
💻
Example
- Monthly Sales:
|
Month |
Jan |
Feb |
Mar |
Apr |
|
Sales |
2000 |
3000 |
2500 |
4000 |
👉 Formula: =HLOOKUP("Mar", A1:E2, 2,
FALSE) → 2500
🎯
Class Activity
- Students create a sales table for 6 months and
use HLOOKUP to find sales for any chosen month.
Day
3 (Wed) – Trial Balance
Objective: Students should record debit and credit transactions and
balance them.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Explain that a trial balance checks if Debit =
Credit.
- Columns: Account, Debit, Credit.
- Use SUM to total Debit & Credit.
💻
Example
|
Account |
Debit |
Credit |
|
Cash |
5000 |
|
|
Purchases |
2000 |
|
|
Sales |
4000 |
|
|
Capital |
3000 |
👉 Total Debit = 7000, Total
Credit = 7000 (Balanced ✅).
🎯
Class Activity
- Students prepare a trial balance with at least 6
accounts.
- Use SUM to check if Debit = Credit.
Day
4 (Thu) – Profit & Loss (P&L) Statement
Objective: Students should prepare a simple P&L Statement.
📝
Teaching Steps
- Explain: Profit = Sales – Expenses.
- Create a table with Income (Sales) and Expenses.
- Use formula: Profit = Total Sales – Total Expenses.
💻
Example
|
Description |
Amount |
|
Sales |
15000 |
|
Rent |
2000 |
|
Wages |
5000 |
|
Utilities |
1000 |
👉 Total Expenses = =SUM(B3:B5) → 8000
👉 Profit = =B2-B6 → 7000
🎯
Class Activity
- Students prepare a P&L Statement for 1 month
with at least 3 income items and 3 expense items.
Day
5 (Fri) – Final Assessment Test
Objective: Assess students’ mastery of general and accounting Excel.
📝
Final Test Task
- Create a Price List Table with at least 5 items
(Code, Item, Price).
- Use VLOOKUP to find the price of 1 item.
- Create a Monthly Sales Table for 6 months.
- Use HLOOKUP to return the sales of April.
- Prepare a Trial Balance with at least 6
accounts.
- Ensure Debit = Credit.
- Prepare a Profit & Loss Statement showing
Total Sales, Total Expenses, and Profit.
✅
Teacher’s Marking Guide
- VLOOKUP applied correctly → 2 marks
- HLOOKUP applied correctly → 2 marks
- Trial Balance balanced → 3 marks
- P&L statement correct → 3 marks
Total = 10 marks
By the end of Week 4, students will be
able to:
- Use VLOOKUP and HLOOKUP.
- Prepare Trial Balance.
- Prepare a Profit & Loss Statement.
- Apply Excel effectively in real accounting scenarios.